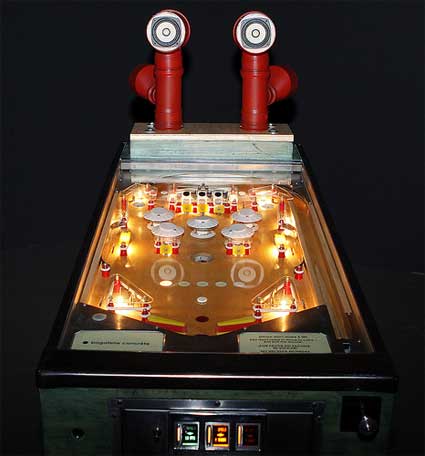
Take two persons whose work in the media art field i’ve been admiring for years. Have their minds communicate for more than a couple of minutes. What is going to happen?

UBERMORGEN.COM (Lizvlx/Hans Bernhard), Psych|OS – Hans 2, 2004. Lambda print on aluminium. 100 x 150 cm. Edition of 5. Private Collection, Brussels / Fabio Paris Art Gallery, Brescia
Yves Bernard is the director of iMAL (interactive Media Art Laboratory), a space dedicated to contemporary artistic and cultural practices emerging from the fusion of computer, telecommunication, network and media. iMAL is the only space that doesn’t put the Belgian french-speaking community i come from to total shame. The presence and recognition of media art varies from country to country but nowhere are these differences as tangible as in Belgium: while Flanders supports media art generously and dynamically for years, the rest of the country believes that media art equals video art. The work of Yves and his team is admired way beyond our national borders but strives to get the attention it deserves in the french-speaking community.
Domenico Quaranta is an art critic and curator living in Brescia, a small-ish city of Northern Italy. He shrugs when i tell him that one day he’ll rule over the art world but that’s because i have more faith in his brilliant writings, impeccable taste and broad culture than he does.

Yves and Domenico took the opportunity offered by Art Brussels, the international contemporary art fair which closed yesterday, to get the eyes of the contemporary art world set onto digital art. With more passion and talent than real budget they curated and organized Holy Fire. Art of the Digital Age, an impressive exhibition featuring the kind of digital artworks susceptible to convince the contemporary art world that digital art should get the place and understanding it deserves in the contemporary art panorama.
To be honest, i needed such exhibition. Last Summer i realized that i was getting a much more fruitful and satisfying art experience at the Venice Biennale than at Ars Electronica. Media art often suffers from faddism and from a series of misunderstandings. For example, i can’t count the number of times i heard someone (or seen an exhibition) confuse “something weird done with technology” with media art.

Joan Leandre, The Kernel Peak: At my Limit(Unknown Universal Series), 2008. Digital Print. 140×102 cm. Edition of 5. Courtesy Project Gentili, Prato
No such risk here. The quality of most of the works on show at iMAL is outstanding. The exhibition counts more than 20 pieces, i’ll just highlight a handful of them:
After a year long immersion in World of Warcraft, Eddo Stern translated the legends, obsessions and symbols of the subculture he had experienced into his art practice. With Emoticon, Stern uses icons and emoticons from online forums to crown and dress a synthetic goddess – herself an icon – which smiles, pouts, frowns, cries and expresses the other emotions at her command in the most languorous way.
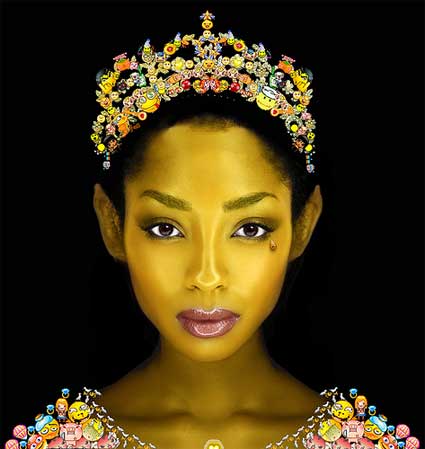

Eddo Stern, Emoticon, 2007. 3D computer animation with sound on 42 inch plasma screen. Running time 3 minutes. Edition of 3. Private Collection, Brussels / Courtesy Postmasters Gallery, New York
For their participation at the Venice Biennale in 2001, Eva and Franco Mattes aka 0100101110101101.org turned a virus Biennale.py into a work of art and spread it from the Slovenian Pavilion on the opening day of the exhibition. The Perpetual Self Dis/Infecting Machine features the Biennale.py virus. Trapped into a computer devoid of any connection to a network, the virus does its best to spread its wings and start its contagious process, but the machine fights back and submits it to a disinfection process. The power game is repeated again and again. Ad vitam eternam.
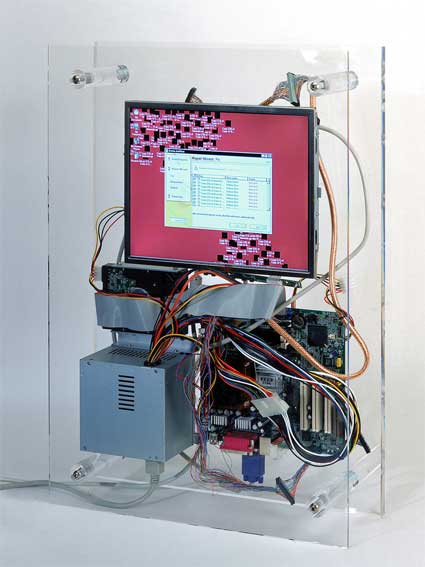

Eva and Franco Mattes (0100101110101101.ORG), Perpetual Self Dis/Infecting Machine, 2001-2003. Custom made computer infected with the virus Biennale.py. 70 x 50 x 13 cm. Courtesy Fabio Paris Art Gallery, Brescia.
Reface [Portrait Sequencer], by Golan Levin and Zachary Lieberman, is a video mash-up that composes endless combinations of visitors’ faces. The installation records and remixes brief video slices of its viewers’ mouths, eyes and brows. Even if visitors move in front of the display the system will line up their face. The images recorded are “edited” by the participants’ own eye blinks. Blinking also triggers the display to advance to the next set of face combinations.

“Reface (Portrait Sequencer)”, 2006, LCD screen, custom software, computer, camera, plexiglass enclosure. Edition of 6. bitforms gallery, New York
Oh, yes! at this point is should also note that in an attempt to explore how new media art, bypassing all the stereotypes connected with its presumed immateriality and difficulties of maintenance, was able to enter the art market, the works on show at Holy Fire come from galleries and collections from around the world (USA, Europe, Russia).
Strangely, the “romantic” idea that to be a valuable artist you have to starve, drink yourself blind with absinthe and die alone in your chambre de bonne is still very much alive and kicking.
Holy Fire shows that it doesn’t have to be the case for media artist by choosing to exhibit only collectible new media artworks already on the art market, in the form of traditional media (prints, videos, sculptures) or customized new media objects.
The art market offers new sources of income for new media artists. Up to now, these have been limited – when they exist – to public funding from institutions and governments, sometimes dictated by politics. An art market can help develop a new economy through direct relations between artists and art consumers, confirming the artists’ social role and the support of the people who are increasingly looking for something different from mass-produced digital gadgets.
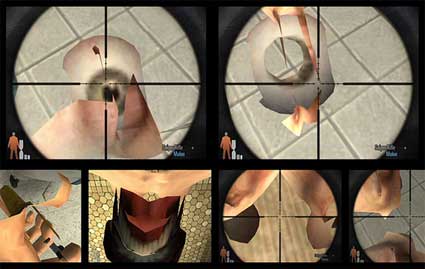
Jodi, Max Payne Cheats Only, 2004. Video installation (2 channels). Private Collection, Brussels
More images from the exhibition.
To investigate the theme explored by Holy Fire: you can either have a look at the discussion about Holy Fire on rhizome and get your hands on the catalog of the exhibition which features opiniated contributions from many protagonists of the media art world.
Even better you can give your view by collaborating to aminima study about the new media art market.

Gazira Babeli. Gaz Of The Desert – Pieta, 2007. Lambda print. 70 x 107 cm. Edition of 3. Collection Marchina-Ghizzardi, Brescia / Courtesy Fabio Paris Art Gallery, Brescia
Holy Fire (yes, the title is inspired by one of Bruce Sterling‘s books) is on view at iMAL (google map), Brussels through April 30, 2008.
Related: walking around Chelsea, A conversation about exhibiting and selling digital fine art.


 Gold – Single TV Commercial – Halo 3 “Diorama”, McCann Worldgroup San Francisco For a full list of winners, Gold through Bronze as well as as Merit, click here then select the link for Download One Show Winners List.
Gold – Single TV Commercial – Halo 3 “Diorama”, McCann Worldgroup San Francisco For a full list of winners, Gold through Bronze as well as as Merit, click here then select the link for Download One Show Winners List.